Installation¶
As of version 0.2.0,
the deproject package can be installed
directly from PyPI. This requires
CIAO 4.11
or later (as installation with pip in earlier versions of
CIAO is not well supported). The module can be used with the
standalone release of
Sherpa,
but it is only useful if Sherpa has been built with
XSPEC support
which is trickier to achieve than we would like.
Requirements¶
The package uses Astropy and SciPy, for units support and cosmological-distance calculations. It is assumed that Matplotlib is available for plotting (which is included in CIAO 4.11).
Using pip¶
CIAO¶
Installation within CIAO requires:
- having sourced the CIAO initialisation script (e.g. ciao.csh or ciao.bash);
- and using a constraints file, to avoid updating NumPy in CIAO.
It should be as simple as:
echo "numpy==1.12.1" > constraints.txt
pip install -c constraints.txt 'astropy<3.1' deproject
Note
The constraints are for CIAO 4.11, please adjust accordingly if using a newer version of CIAO (the Astropy restriction is because version 3.1 requires NumPy version 1.13 or later but CIAO 4.11 is shipped with NumPy version 1.12).
Standalone¶
When using the standalone Sherpa intallation, the following should be all that is required:
pip install deproject
Manual installation¶
The source is available on github at https://github.com/sherpa-deproject/deproject, with releases available at https://github.com/sherpa-deproject/deproject/releases.
After downloading the source code (whether from a release or by cloning the repository) and moving into the directory (deproject-<version> or deproject), installation just requires:
python setup.py install
Note
This command should only be run after setting up CIAO or whatever Python environment contains your Standalone Sherpa installation.
Test¶
The source installation includes a basic test suite, which can be run with either
pytest
or
python setup.py test
Example data¶
The example data can be download from either http://cxc.cfa.harvard.edu/contrib/deproject/downloads/m87.tar.gz or from GitHub. The source distribution includes scripts - in the examples directory - that can be used to replicate both the basic M87 example and the follow-on example combining annuli.
As an example (from within an IPython session, such as the Sherpa shell in CIAO):
>>> %run fit_m87.py
...
... a lot of screen output will whizz by
...
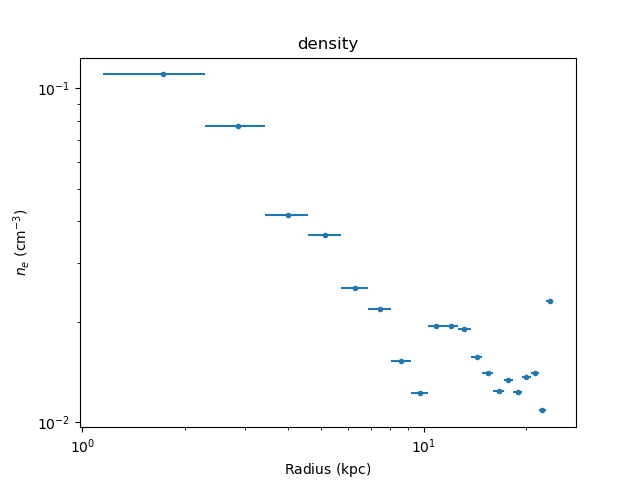
The current density estimates can then be displayed with:
>>> dep.density_plot()
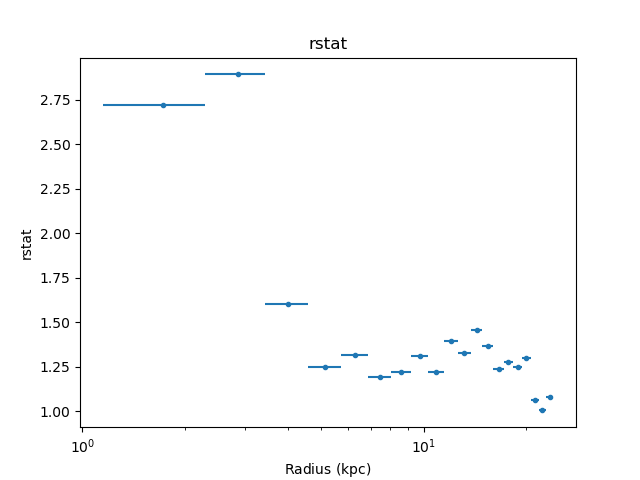
the reduced-statistic for the fit to each shell with:
>>> dep.fit_plot('rstat')
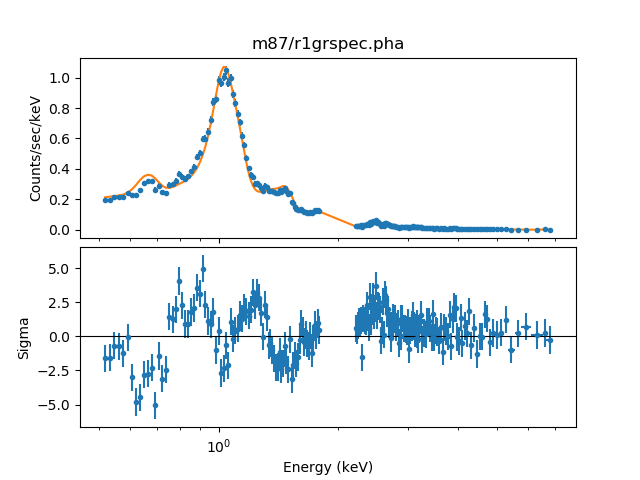
and the fit results for the first annulus can be displayed using the Sherpa functions:
>>> set_xlog()
>>> plot_fit_delchi(0)